Monitoring and Tracing
If something is not working as it should within your GraphQL gateway, you would not want it to go unnoticed.
Monitoring and tracing are essential for debugging and understanding the performance of your gateway.
You can use Gateway plugins to trace and monitor your gateway’s execution flow together with all outgoing HTTP calls and internal query planning.
Healthcheck
Hive Gateway is aware of the usefulness of a health check and gives the user maximum possibilities to use the built-in check.
There are two types of health checks: liveliness and readiness, they both are a health check but convey a different meaning:
- Liveliness checks whether the service is alive and running
- Readiness checks whether the upstream services are ready to perform work and execute GraphQL operations
The difference is that a service can be live but not ready - for example, server has started and is accepting requests (alive), but the read replica it uses is still unavailable (not ready).
Both endpoints are enabled by default.
Liveliness
By default, you can check whether the gateway is alive by issuing a request to the /healthcheck
endpoint and expecting the response 200 OK. A successful response is just 200 OK without a body.
You can change this endpoint through the healthCheckEndpoint option:
import { defineConfig } from '@graphql-hive/gateway'
export const gatewayConfig = defineConfig({
healthCheckEndpoint: '/healthcheck'
})Readiness
For readiness check, Hive Gateway offers another endpoint (/readiness) which checks whether the
services powering your gateway are ready to perform work. It returns 200 OK if all the services
are ready to execute GraphQL operations.
It returns 200 OK if all the services are ready to perform work.
You can customize the readiness check endpoint through the readinessCheckEndpoint option:
import { defineConfig } from '@graphql-hive/gateway'
export const gatewayConfig = defineConfig({
readinessCheckEndpoint: '/readiness'
})OpenTelemetry Traces
Hive Gateway supports OpenTelemetry for tracing and monitoring your gateway.
OpenTelemetry is a set of APIs, libraries, agents, and instrumentation to provide observability to your applications.
The following are available to use with this plugin:
- HTTP request: tracks the incoming HTTP request and the outgoing HTTP response
- GraphQL Lifecycle tracing: tracks the GraphQL execution lifecycle (parse, validate and execution).
- Upstream HTTP calls: tracks the outgoing HTTP requests made by the GraphQL execution.
- Context propagation: propagates the trace context between the incoming HTTP request and the outgoing HTTP requests.
- Custom Span and attributes: Add your own business spans and attributes from your own plugin.
- Logs and Traces correlation: Rely on standard OTEL shared context to correlate logs and traces
OpenTelemetry Setup
For the OpenTelemetry tracing feature to work, OpenTelemetry JS API must be setup.
We recommend to place your OpenTelemetry setup in a telemetry.ts file that will be your first
import in your gateway.config.ts file. This allow instrumentations to be registered (if any)
before any other packages are imported.
For ease of configuration, we provide a openTelemetrySetup function, with sensible default and
straightforward API compatible with all runtimes.
But this utility is not mandatory, you can use any setup relevant to your specific use case and infrastructure.
The most commonly used otel packages are available when using Hive Gateway with CLI. Please switch to programmatic usage if you need more packages.
Please refer to opentelemetry-js documentation for
more details about OpenTelemetry setup and API.
Basic usage
This configuration API still rely on official @opentelemetry/api package, which means you can use
any official or standard compliant packages with it.
You will have to pick a
Context Manager (we recommend
to use AsyncLocalStorageContextManager from @opentelemetry/context-async-hooks if your runtime
supports AsyncLocalStorage API), and a trace exporter depending on your traces backend (probably
@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http).
npm i @opentelemetry/context-async-hooks @opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-httpDepending on your usage, you will have to import openTelemetrySetup from a different module:
- CLI usage:
@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup - Programmatic usage :
@graphql-hive/plugin-opentelemetry/setup
// For CLI usage
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
// For Programmatic usage
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/plugin-opentelemetry/setup'
import { AsyncLocalStorageContextManager } from '@opentelemetry/context-async-hooks'
import { OTLPTraceExporter } from '@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-http'
openTelemetrySetup({
// Mandatory: It depends on the available API in your runtime.
// We recommend AsyncLocalStorage based manager when possible.
// `@opentelemetry/context-zone` is also available for other runtimes.
// Pass `false` to disable context manager usage.
contextManager: new AsyncLocalStorageContextManager(),
traces: {
// Define your exporter, most of the time the OTLP HTTP one. Traces are batched by default.
exporter: new OTLPTraceExporter({ url: process.env['OTLP_URL'] }),
// You can easily enable a console exporter for quick debug
console: process.env['DEBUG_TRACES'] === '1'
}
})After configuring and setting up the telemetry, make sure to import it as the first import in your
gateway.config.ts file and enable OpenTelemetry tracing:
import './telemetry'
import { defineConfig } from '@graphql-hive/gateway'
export const gatewayConfig = defineConfig({
openTelemetry: {
traces: true
}
})Service name and version
You can provide a service name, either by using standard OTEL_SERVICE_NAME and
OTEL_SERVICE_VERSION or by providing them programmatically via setup options
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
openTelemetrySetup({
resource: {
serviceName: 'my-service',
serviceVersion: '1.0.0'
}
})Custom resource attributes
Resource attributes can be defined by providing a Resource instance to the setup resource
option.
This resource will be merged with the resource created from env variables, which means
service.name and service.version are not mandatory if already provided through environment
variables.
npm i @opentelemetry/resourcesimport { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
import { resourceFromAttributes } from '@opentelemetry/resources'
openTelemetrySetup({
resource: resourceFromAttributes({
'custom.attribute': 'my custom value'
})
})Trace Exporter, Span Processors and Tracer Provider
Exporters are responsible of storing the traces recorded by OpenTelemetry. There is a large existing
range of exporters, Hive Gateway is compatible with any exporter using @opentelemetry/api standard
OpenTelemetry implementation.
Span Processors are responsible of processing recorded spans before they are stored. They generally take an exporter in parameter, which is used to store processed spans.
Tracer Provider is responsible of creating Tracers that will be used to record spans.
You can setup OpenTelemetry by providing either:
- a Trace Exporter. A Span processor and a Tracer Provider will be created for you, with sensible production defaults like trace batching.
- a list of Span Processors. This gives you more control, and allows to define more than one exporter. The Tracer Provider will be created for you.
- a Tracer Provider. This is the manual setup mode where nothing is created automatically. The Tracer Provider will just be registered.
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
import { AsyncLocalStorageContextManager } from '@opentelemetry/context-async-hooks'
openTelemetrySetup({
contextManager: new AsyncLocalStorageContextManager(),
traces: {
// Define your exporter, most of the time the OTLP HTTP one. Traces are batched by default.
exporter: ...,
// To ease debug, you can also add a non-batched console exporter easily with `console` option
console: true,
},
})
// or
openTelemetrySetup({
contextManager: new AsyncLocalStorageContextManager(),
traces: {
// Define your span processors.
processors: [...],
},
})
// or
openTelemetrySetup({
contextManager: new AsyncLocalStorageContextManager(),
traces: {
// Define your span processors.
tracerProvider: ...,
},
})Hive Gateway CLI embeds every official OpenTelemetry exporters. Please switch manual deployment or programmatic usage to install a non-official exporter.
A simple exporter that writes the spans to the stdout of the process. It is mostly used for
debugging purpose.
See official documentation for more details.
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
openTelemetrySetup({
contextManager: new AsyncLocalStorageContextManager(),
traces: {
console: true
}
})Context Propagation
By default, Hive Gateway will propagate the trace context between the incoming HTTP request and the outgoing HTTP requests using standard Baggage and Trace Context propagators.
You can configure the list of propagators that will be used. All official propagators are bundled with Hive Gateway CLI. To use other non-official propagators, please switch to manual deployment.
You will also have to pick a Context Manager. It will be responsible to keep track of the current
OpenTelemetry Context at any point of program. We recommend using the official
AsyncLocalStorageContextManager from @opentelemetry/context-async-hooks when AsyncLocalStorage
API is available. In other cases, you can either try @opentelemetry/context-zone, or pass null
to not use any context manager.
If no Context Manager compatible with async is registered, automatic parenting of custom spans will
not work. You will have to retrieve the current OpenTelemetry context from the GraphQL context, or
from the getActiveContext method of the plugin instance.
npm i @opentelemetry/context-async-hooks @opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-grpc @opentelemetry/propagator-b3import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
import { AsyncLocalStorageContextManager } from '@opentelemetry/context-async-hooks'
import { OTLPTraceExporter } from '@opentelemetry/exporter-trace-otlp-grpc'
import { B3Propagator } from '@opentelemetry/propagator-b3'
openTelemetrySetup({
contextManager: new AsyncLocalStorageContextManager(),
traces: {
exporter: new OTLPTraceExporter({ url: 'http://<otlp-endpoint>:4317' })
},
propagators: [new B3Propagator()]
})Span Batching
By default, if you provide only a Trace Exporter, it will be wrapped into a BatchSpanProcessor to
batch spans together and reduce the number of request to you backend.
This is an important feature for a real world production environment, and you can configure its behavior to exactly suites your infrastructure limits.
By default, the batch processor will send the spans every 5 seconds or when the buffer is full.
The following configuration are allowed:
true(default): enables batching and useBatchSpanProcessordefault config.object: enables batching and useBatchSpanProcessorwith the provided configuration.false- disables batching and useSimpleSpanProcessor
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
openTelemetrySetup({
traces: {
exporter: ...,
batching: {
exportTimeoutMillis: 30_000, // Default to 30_000ms
maxExportBatchSize: 512, // Default to 512 spans
maxQueueSize: 2048, // Default to 2048 spans
scheduledDelayMillis: 5_000, // Default to 5_000ms
}
},
})You can learn more about the batching options in the Picking the right span processor page.
Sampling
When your gateway have a lot of traffic, tracing every requests can become a very expensive approach.
A mitigation for this problem is to trace only some requests, using a strategy to choose which request to trace or not.
The most common strategy is to combine both a parent first (a span is picked if parent is picked) and a ratio based on trace id (each trace, one by request, have a chance to be picked, with a given rate).
By default, all requests are traced. You can either provide you own Sampler, or provide a sampling rate which will be used to setup a Parent + TraceID Ratio strategy.
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
import { JaegerRemoteSampler } from '@opentelemetry/sampler-jaeger-remote'
import { AlwaysOnSampler } from '@opentelemetry/sdk-trace-base'
openTelemetrySetup({
// Use Parent + TraceID Ratio strategy
samplingRate: 0.1,
// Or use a custom Sampler
sampler: new JaegerRemoteSampler({
endpoint: 'http://your-jaeger-agent:14268/api/sampling',
serviceName: 'your-service-name',
initialSampler: new AlwaysOnSampler(),
poolingInterval: 60000 // 60 seconds
})
})Limits
To ensure that you don’t overwhelm your tracing ingestion infrastructure, you can set limits for both cardinality and amount of data the OpenTelemetry SDK will be allowed to generate.
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
openTelemetrySetup({
generalLimits: {
//...
},
traces: {
spanLimits: {
//...
}
}
})Configuration
Once you have an OpenTelemetry setup file, you must import it from you gateway.config.ts file. It
must be the very first import so that any other package relying on OpenTelemetry have access to the
correct configuration.
You can then enable OpenTelemetry Tracing support in the Gateway configuration.
with CLI, you can either enable OpenTelemetry tracing by using --opentelemetry option or by using
the configuration file.
hive-gateway supergraph --opentelemetryOpenTelemetry Context
To correlate all observability events (like tracing, metrics, logs…), OpenTelemetry have a global and standard Context API.
This context also allows to keep the link between related spans (for parenting or linking of spans).
You can configure the behavior of the plugin with this context.
const openTelemetryConfig = {
useContextManager: true, // If false, the parenting of spans will not rely on OTEL Context
inheritContext: true, // If false, the root span will not be based on OTEL Context, it will always be a root span
propagateContext: true // If false, the context will not be propagated to subgraphs
})OpenTelemetry Diagnostics
If you encounter an issue with you OpenTelemetry setup, you can enable the Diagnostics API. This
will enable logging of OpenTelemetry SDK based on OTEL_LOG_LEVEL env variable.
By default, Hive Gateway configure the Diagnostics API to output logs using Hive Gateway’s logger.
You can disable this using configureDiagLogger option.
const openTelemetryConfig = {
// Use the default DiagLogger, which outputs logs directly to stdout
configureDiagLogger: false
}Graceful shutdown
Since spans are batched by default, it is possible to miss some traces if the batching processor is not properly flushed when the process exits.
To avoid this kind of data loss, Hive Gateway is calling forceFlush method on the registered
Tracer Provider by default. You can customize which method to call or entirely disable this behavior
by using the flushOnDispose option.
const openTelemetryConfig = {
// Disable the auto-flush on shutdown
flushOnDispose: false,
// or call a custom method
flushOnDispose: 'flush'
}Tracer
By default, Hive Gateway will create a tracer named gateway. You can provide your own tracer if
needed.
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
tracer: trace.getTracer('my-custom-tracer')
}
}Reported Spans
The plugin exports the following OpenTelemetry Spans:
Background Spans
Gateway Initialization
By default, the plugin will create a span from the start of the gateway process to the first schema load.
All spans happening during this time will be parented under this initialization span, including the schema loading span.
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.initialization to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
initialization: false
}
}
}Schema Loading
By default, the plugin will create a span covering each loading of a schema. It can be useful when polling or file watch is enabled to identify when the schema changes.
Schema loading in Hive Gateway can be lazy, which means it can be triggered as part of the handling of a request. If it happens, the schema loading span will be added as a link to the current span.
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.schema to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
schema: false
}
}
}Request Spans
HTTP Request
This span is created for each incoming HTTP request, and acts as a root span for the entire request. Disabling this span will also disable the other hooks and spans.
By default, the plugin will create a root span for the HTTP layer as a span (<METHOD> /path, eg.
POST /graphql) with the following attributes:
http.method: The HTTP methodhttp.url: The HTTP URLhttp.route: The HTTP status codehttp.scheme: The HTTP schemehttp.host: The HTTP hostnet.host.name: The hostnamehttp.user_agent: The HTTP user agent (based on theUser-Agentheader)http.client_ip: The HTTP connecting IP (based on theX-Forwarded-Forheader)
And the following attributes for the HTTP response:
http.status_code: The HTTP status code
An error in the this phase will be reported as an error
span with the HTTP
status text and as an OpenTelemetry
Exception.
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.http to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
http: false
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.http configuration to a function:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
http: ({ request }) => {
// Filter the spans based on the request
return true
}
}
}
}GraphQL Operation
This span is created for each GraphQL operation found in incoming HTTP requests, and acts as a parent span for the entire graphql operation. Disabling this span will also disable the other hooks and spans related to the execution of operation.
By default, the plugin will create a span for the GraphQL layer as a span
(graphql.operation <operation name> or graphql.operation for unexecutable operations) with the
following attributes:
graphql.operation.type: The type of operation (query,mutationorsubscription).graphql.operation.name: The name of the operation to execute,Anonymousfor operations without name.graphql.document: The operation document as a GraphQL string
An error in the parse phase will be reported as an error
span, including the
error message and as an OpenTelemetry
Exception.
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.graphql to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
traces: {
spans: {
graphql: false
}
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.graphql configuration to a function which
takes the GraphQL context as parameter:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
graphql: ({ context }) => {
// Filter the span based on the GraphQL context
return true
}
}
}
}GraphQL Parse
By default, the plugin will report the validation phase as a span (graphql.validate) with the
following attributes:
graphql.document: The GraphQL query stringgraphql.operation.name: The operation name
If a parsing error is reported, the following attribute will also be present:
graphql.error.count:1if a parse error occurred
An error in the parse phase will be reported as an error
span, including the
error message and as an OpenTelemetry
Exception.
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.graphqlParse to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
graphqlParse: false
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.graphqlParse configuration to a function:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
graphqlParse: ({ context }) => {
// Filter the spans based on the GraphQL context
return true
}
}
}
}GraphQL Validate
By default, the plugin will report the validation phase as a span (graphql.validate) with the
following attributes:
graphql.document: The GraphQL query stringgraphql.operation.name: The operation name
If a validation error is reported, the following attribute will also be present:
graphql.error.count: The number of validation errors
An error in the validate phase will be reported as an error
span, including the
error message and as an OpenTelemetry
Exception.
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.graphqlValidate to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
graphqlValidate: false
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.graphqlValidate configuration to a
function:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
graphqlValidate: ({ context }) => {
// Filter the spans based on the GraphQL context
return true
}
}
}
}Graphql Context Building
By default, the plugin will report the validation phase as a span (graphql.context). This span
doesn’t have any attribute.
An error in the context building phase will be reported as an error
span, including the
error message and as an OpenTelemetry
Exception.
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.graphqlContextBuilding to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
graphqlContextBuilding: false
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.graphqlContextBuilding configuration to a
function:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
graphqlContextBuilding: ({ context }) => {
// Filter the spans based on the GraphQL context
return true
}
}
}
}GraphQL Execute
By default, the plugin will report the execution phase as a span (graphql.execute) with the
following attributes:
graphql.document: The GraphQL query stringgraphql.operation.name: The operation name (Anonymousfor operations without name)graphql.operation.type: The operation type (query/mutation/subscription)
If an execution error is reported, the following attribute will also be present:
graphql.error.count: The number of errors in the execution result
An error in the execute phase will be reported as an error
span, including the
error message and as an OpenTelemetry
Exception.
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.graphqlExecute to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
graphqlExecute: false
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.graphqlExecute configuration to a
function:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
graphqlExecute: ({ context }) => {
// Filter the spans based on the GraphQL context
return true
}
}
}
}Subgraph Execute
By default, the plugin will report the subgraph execution phase as a client span
(subgraph.execute) with the following attributes:
graphql.document: The GraphQL query string executed to the upstreamgraphql.operation.name: The operation namegraphql.operation.type: The operation type (query/mutation/subscription)gateway.upstream.subgraph.name: The name of the upstream subgraph
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.subgraphExecute to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
subgraphExecute: false
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.subgraphExecute configuration to a
function:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
subgraphExecute: ({ executionRequest, subgraphName }) => {
// Filter the spans based on the target SubGraph name and the Execution Request
return true
}
}
}
}Upstream Fetch
By default, the plugin will report the upstream fetch phase as a span (http.fetch) with the
information about outgoing HTTP calls.
The following attributes are included in the span:
http.method: The HTTP methodhttp.url: The HTTP URLhttp.route: The HTTP status codehttp.scheme: The HTTP schemenet.host.name: The hostnamehttp.host: The HTTP hosthttp.request.resend_count: Number of retry attempt. Only present starting from the first retry.
And the following attributes for the HTTP response:
http.status_code: The HTTP status code
An error in the fetch phase (including responses with a non-ok status code) will be reported as an
error span, including
the error message and as an OpenTelemetry
Exception.
You may disable this by setting traces.spans.upstreamFetch to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
upstreamFetch: false
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.upstreamFetch configuration to a
function:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
spans: {
upstreamFetch: ({ executionRequest }) => {
// Filter the spans based on the Execution Request
return true
}
}
}
}Reported Events
The plugin exports the following OpenTelemetry Events.
Events are attached to the current span, meaning that they will be attached to your custom spans if you use them. It also means that events can be orphans if you didn’t properly setup an async compatible Context Manager
Cache Read and Write
By default, the plugin will report any cache read or write as an event. The possible event names are:
gateway.cache.miss: A cache read happened, but the key didn’t match any entitygateway.cache.hit: A cache read happened, and the key did match an entitygateway.cache.write: A new entity have been added to the cache store
All those events have the following attributes:
gateway.cache.key: The key of the cache entrygateway.cache.ttl: The ttl of the cache entry
You may disable this by setting traces.events.cache to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
events: {
cache: false
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.upstreamFetch configuration to a
function:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
events: {
cache: ({ key, action }) => {
// Filter the event based on action ('read' or 'write') and the entity key
return true
}
}
}
}Cache Error
By default, the plugin will report any cache error as an event (gateway.cache.error). This events
have the following attributes:
gateway.cache.key: The key of the cache entrygateway.cache.ttl: The ttl of the cache entrygateway.cache.action: The type of action (readorwrite)exception.type: The type of error (thecodeif it exists, the message otherwise)exception.message: The message of the errorexception.stacktrace: The error stacktrace as a string
You may disable this by setting traces.events.cache to false:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
events: {
cache: false
}
}
}Or, you may filter the spans by setting the traces.spans.upstreamFetch configuration to a
function:
const openTelemetryConfig = {
traces: {
events: {
cache: ({ key, action }) => {
// Filter the event based on action ('read' or 'write') and the entity key
return true
}
}
}
}Custom spans
Hive Gateway relies on official OpenTelemetry API, which means it is compatible with
@opentelemetry/api.
You can use any tool relying on it too, or directly use it to create your own custom spans.
To parent spans correctly, an async compatible Context Manager is highly recommended, but we also
provide an alternative if your runtime doesn’t implement AsyncLocalStorage or you want to avoid
the related performance cost.
If you are using an async compatible context manager, you can simply use the standard
@opentelemetry/api methods, as shown in
OpenTelemetry documentation.
The Gateway’s tracer is available can be accessed through the Hive Gateway OpenTelemetry API
(@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/api).
Note that the tracer will be defined only once the OpenTelemetry plugin has been instantiated,
which means it will not be defined at import time or if openTelemetry option is false.
You can also create your own tracer instead of reusing the Gateway one.
import { defineConfig } from '@graphql-hive/gateway'
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
import { hive } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/api'
import { AsyncLocalStorageContextManager } from '@opentelemetry/context-async-hooks'
import { useGenericAuth } from '@envelop/generic-auth'
openTelemetrySetup({
contextManager: new AsyncLocalStorageContextManager(),
traces: { console: true },
})
export const gatewayConfig = defineConfig({
openTelemetry: {
traces: true,
},
genericAuth: {
resolveUserFn: (context) => {
// `startActiveSpan` will rely on the current context to parent the new span correctly
// You can also use your own tracer instead of Hive Gateway's one.
return hive.tracer!.startActiveSpan('users.fetch', (span) => {
const user = await fetchUser(extractUserIdFromContext(context))
span.end();
return user
})
}
},
})Custom Span Attributes, Events and Links
You can add custom attribute to Hive Gateway’s spans by using the standard @opentelemetry/api
package. You can use the same package to record custom
Events or
Links.
This can be done by getting access to the current span.
If you have an async compatible Context Manager setup, you can use the standard OpenTelemetry API to retrieve the current span as shown in OpenTelemetry documentation.
Otherwise, Hive Gateway provide it’s own cross-runtime Context tracking mechanism. In this case, you
can use
trace.getSpan standard function
to get access to the current span.
If you are using an async compatible context manager, you can simply use the standard
@opentelemetry/api methods, as shown in
OpenTelemetry documentation.
import { defineConfig } from '@graphql-hive/gateway'
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/setup'
import { trace } from '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/api'
import { AsyncLocalStorageContextManager } from '@opentelemetry/context-async-hooks'
import { useGenericAuth } from '@envelop/generic-auth'
openTelemetrySetup({
contextManager: new AsyncLocalStorageContextManager(),
traces: { console: true },
})
export const gatewayConfig = defineConfig({
openTelemetry: {
traces: true,
},
plugins: () => [
useGenericAuth({
resolveUserFn: (context) => {
const span = trace.getActiveSpan();
const user = await fetchUser(extractUserIdFromContext(context))
span.setAttribute('user.id', user.id);
return user
}
}),
],
})Access root spans
Sometimes, you don’t want to add the custom attribute on the current span, but on one of the root spans (http, operation, subgraph execution).
You can access those spans by using getHttpContext(request), getOperationContext(context) and
getExecutionRequestContext(executionRequest) functions from
@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/api.
They are also accessible under openTelemetry key of the graphql and configuration context, and on
the plugin. When using the graphql context, the argument is optional and functions will return the
current appropriate root context.
import { hive, trace } '@graphql-hive/gateway/opentelemetry/api'
import { defineConfig } from '@graphql-hive/gateway'
export config gatewayConfig = defineConfig({
openTelemetry: {
traces: true
},
plugin: () => [{
onRequest({ request }) {
const httpSpan = trace.getSpan(hive.getHttpContext(request))
},
onExecute({ context }) {
const operationSpan = trace.getSpan(hive.getOperationContext(context))
},
onSubgraphExecute({ executionRequest }) {
const executionRequestSpan = trace.getSpan(hive.getExecutionRequestContext(executionRequest))
},
}]
})Troubleshooting
The default behavior of the plugin is to log errors and warnings to the console.
You can customize this behavior by changing the value of the
OTEL_LOG_LEVEL
environment variable on your gateway process/runtime.
In addition, you can use the stdout exporter to log the traces to the console:
// For CLI usage
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/plugin-opentelemetry/setup'
// For Programmatic usage
import { openTelemetrySetup } from '@graphql-hive/plugin-opentelemetry/setup'
import { AsyncLocalStorageContextManager } from '@opentelemetry/context-async-hooks'
openTelemetrySetup({
contextManager: new AsyncLocalStorageContextManager(),
traces: {
console: true
}
})This will log the traces to the console, which can be useful for debugging and troubleshooting.
Prometheus Metrics
Prometheus is a utility for producing, scraping and storing metrics from services and utilities.
You can use this feature of the gateway to expose and collect metrics from all phases of your GraphQL execution including internal query planning and outgoing HTTP requests.
The metrics gathered are then exposed in a format that Prometheus can scrape on a regular basis on
an HTTP endpoint (/metrics by default).
Usage Example
import { defineConfig } from '@graphql-hive/gateway'
export const gatewayConfig = defineConfig({
prometheus: {
// Enable the metrics you want to expose
// The following represent the default config of the plugin.
metrics: {
graphql_gateway_fetch_duration: true,
graphql_gateway_subgraph_execute_duration: true,
graphql_gateway_subgraph_execute_errors: true,
graphql_envelop_deprecated_field: true,
graphql_envelop_request: true,
graphql_envelop_request_duration: true,
graphql_envelop_request_time_summary: true,
graphql_envelop_phase_parse: true,
graphql_envelop_phase_validate: true,
graphql_envelop_phase_context: true,
graphql_envelop_error_result: true,
graphql_envelop_phase_execute: true,
graphql_envelop_phase_subscribe: true,
graphql_envelop_schema_change: true,
graphql_yoga_http_duration: true
}
}
})You can now start your Hive Gateway and make some requests to it. The plugin will start collecting
metrics, and you can access them by visiting the /metrics endpoint.
In most cases, you’ll need to setup a Prometheus server to scrape the metrics from your gateway, we recommend using the official Prometheus Server or tools like Vector.
Grafana Dashboard
If you are using Grafana to visualize your metrics, you can import this pre-configured Grafana dashboard from Grafana’s marketplace, or you can use/import this dashboard JSON file directly to easily visualize the metrics for your gateway.
For additional instructions, please refer to Import dashboards instruction in Grafana documentation.
Reported Metrics
You will find the timing of each GraphQL execution phase. If you are not familiar with the lifecycle of a GraphQL operation in the gateway, please refer to the Plugin Lifecycle page. Each plugin hook has a corresponding metric which tracks timings as histograms or summary. You will also find some counters to track the number of requests, errors, and other useful information.
To enable a metric, set the corresponding option to true in the metrics option’s object. You can
also provide a string to customize the metric name, or an object to provide more options (see
siimon/prom-client documentation).
Histogram metrics can be passed an array of numbers to configure buckets.
graphql_yoga_http_duration (default: enabled, type: Histogram)
This metric tracks the duration of incoming (downstream) HTTP requests. It reports the time spent to process each incoming request as a histogram.
It is useful to track the responsiveness of your gateway. A spike in this metric could indicate a performance issue and that further investigation is needed.
Please note that this metric is not specific to GraphQL, it tracks all incoming HTTP requests.
You can use labels to have a better understanding of the requests and group them together. A common
filter is to include only statusCode with 200 value and method with POST (the default method
for GraphQL requests, but it can also be GET depending on your client setup) value to get
execution time of successful GraphQL requests only.
This metric includes some useful labels to help you identify requests and group them together.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
method | The HTTP method used to request the gateway endpoint. Since GraphQL usually only uses POST requests, this can be used to filter out GraphiQL-related requests. It can be any HTTP verb, including disallowed ones. Which means this metric can also be used to track malformed or malicious requests. |
statusCode | The HTTP status code returned by the gateway. You probably want to filter out non- 200 responses to have a view of the successful requests.This can help you identify which requests are failing and why. Since GraphQL errors are returned as 200 OK responses, this can be useful to track errors that are not related to the GraphQL, like malformed requests. |
operationName | If available, the name of the GraphQL operation requested, otherwise Anonymous.This can help you identify which operations are slow or failing. We recommend you always provide an operation name to your queries and mutations to help performance analysis and bug tracking. |
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. It can be one of query, mutation, or subscription.This can help you differentiate read and write performance of the system. It can for example help understand cache impact. |
url | The URL of the request. Useful to filter graphql endpoint metrics (/graphql by default). |
graphql_gateway_fetch_duration (default: enabled, type: Histogram)
This metric tracks the duration of outgoing HTTP requests. It reports the time spent on each request
made using the fetch function provided by the gateway. It is reported as a
histogram.
This metric can provide insights into the network usage of your gateway. It does not only include requests made to resolve GraphQL operation responses, but also include any other outgoing HTTP requests made by the gateway or one of its plugins. It will for example include requests made to fetch the supergraph schema from the configured Schema Registry.
These metrics include some useful labels to help you identify requests and group them together.
Since they can be heavy, requestHeaders and responseHeaders are disabled by default. You can
either set those options to true in the label configuration object to include all headers in the
label, but you can also provide a list of header names to include.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
url | The URL of the upstream request. |
method | The HTTP method of the upstream request. |
statusCode | The status code of the upstream response. |
statusText | The status text of the upstream response. |
requestHeaders | Disabled by default. A JSON encoded object containing the headers of the upstream request. |
responseHeaders | Disabled by default. A JSON encoded object containing the headers of the upstream response. |
graphql_gateway_subgraph_execute_duration (default: enabled, type: Histogram)
This metric tracks the duration of subgraph execution. It reports the time spent on each subgraph queries made to resolve incoming operations as a histogram.
This metric can provide insights into how the time is spent to resolve queries. It can help you identify bottlenecks in your subgraphs.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
subgraphName | The name of the targeted subgraph. |
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation executed by the subgraph. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation executed by the subgraph. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_gateway_subgraph_execute_errors (default: enabled, type: Counter)
This metric tracks the number of errors that occurred during the subgraph execution. It counts all errors found in the response returned by the subgraph execution. It is exposed as a counter.
This metric can help you identify subgraphs that are failing to execute operations. It can help identify issues with the subgraph itself or the communication between the gateway and the subgraph.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
subgraphName | The name of the targeted subgraph. |
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation executed by the subgraph. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation executed by the subgraph. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_phase_parse (default: enabled, type: Histogram)
This metric tracks the duration of the parse phase of the GraphQL execution. It reports the time
spent parsing the incoming GraphQL operation. It is reported as a
histogram.
Since you don’t have control over the parsing phase, this metric is mostly useful to track potential attacks. A spike in this metric could indicate someone is trying to send malicious operations to your gateway.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_phase_validate (default: enabled, type: Histogram)
This metric tracks the duration of the validate phase of the GraphQL execution. It reports the
time spent validating the incoming GraphQL operation. It is reported as a
histogram.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_phase_context (default: enabled, type: Histogram)
This metric tracks the duration of the context phase of the GraphQL execution. It reports the time
spent building the context object that will be passed to the executors. It is reported as a
histogram.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_phase_execute (default: enabled, type: Histogram)
This metric tracks the duration of the execute phase of the GraphQL execution. It reports the time
spent actually resolving the response of the incoming operation. This includes the gathering of all
the data from all sources required to construct the final response. It is reported as a
histogram.
It is the metric that will give you the most insights into the performance of your gateway, since this is where most of the work is done.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_phase_subscribe (default: enabled, type: Histogram)
This metric tracks the duration of the subscribe phase of the GraphQL execution. It reports the
time spent initiating a subscription (which doesn’t include actually sending the first response). It
is reported as a histogram.
It will notably include the time spent to setup upstream subscriptions with appropriate transport for each source.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_request_duration (default: enabled, type: Histogram)
This metric tracks the duration of the complete GraphQL operation execution. It reports the time spent in the GraphQL specific processing, excluding the HTTP-level processing. It is reported as a histogram.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_request_time_summary (default: enabled, type: Summary)
This metric provides a summary of the time spent on the GraphQL operation execution. It reports the
same timing than graphql_envelop_request_duration but as a
summary.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_error_result (default: enabled, type: Counter)
This metric tracks the number of errors that was returned by the GraphQL execution.
Similarly to graphql_gateway_subgraph_execute_errors,
it counts all errors found in the final response constructed by the gateway after it gathered all
subgraph responses, but it also includes errors from other GraphQL processing phases (parsing,
validation and context building). It is exposed as a
counter.
Depending on the phase when the error occurred, some labels may be missing. For example, if the
error occurred during the context phase, only the phase label will be present.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
path | The path of the field that caused the error. It can be undefined if the error is not related to a given field. |
phase | The phase of the GraphQL execution where the error occurred. It can be parse, validate, context, execute (for every operation types including subscriptions). |
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_request (default: enabled, type: Counter)
This metric tracks the number of GraphQL operations executed. It counts all operations, either failed or successful, including subscriptions. It is exposed as a counter.
It can differ from the number reported by
graphql_yoga_http_duration_sum because a single HTTP request can
contain multiple GraphQL operations if batching has been enabled.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_deprecated_field (default: enabled, type: Counter)
This metric tracks the number of deprecated fields used in the GraphQL operation.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
fieldName | The name of the deprecated field that has been used. |
typeName | The name of the parent type of the deprecated field that has been used. |
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
graphql_envelop_schema_change (default: enabled, type: Counter)
This metric tracks the number of schema changes that have occurred since the gateway started. When polling is enabled, this will include the schema reloads.
If you are using a plugin that modifies the schema on the fly, be aware that this metric will also include updates made by those plugins. Which means that one schema update can actually trigger multiple schema changes.
graphql_envelop_execute_resolver (default: disabled, type: Histogram)
Enabling resolvers level metrics will introduce significant overhead. It is recommended to enable this metric only for debugging purposes.
This metric tracks the duration of each resolver execution. It reports the time spent only on additional resolvers, not on fields that are resolved by a subgraph. It is up to the subgraph server to implement resolver level metrics, the gateway can’t remotely track their execution time.
| Label | Description |
|---|---|
operationType | The type of the GraphQL operation requested. This can be one of query, mutation, or subscription. |
operationName | The name of the GraphQL operation requested. It will be Anonymous if no operationName is found. |
fieldName | The name of the field being resolved. |
typeName | The name of the parent type of the field being resolved. |
returnType | The name of the return type of the field being resolved. |
Filter resolvers to instrument
To mitigate the cost of instrumenting all resolvers, you can explicitly list the fields that should
be instrumented by providing a list of field names to the instrumentResolvers option.
It is a list of strings in the form of TypeName.fieldName. For example, to instrument the hello
root query, you would use Query.hello.
You can also use wildcards to instrument all the fields for a type. For example, to instrument all
root queries, you would use Query.*.
Troubleshooting
You can observe and troubleshoot the metrics by visiting the /metrics endpoint of your gateway.
Run your gateway and execute a few GraphQL operations to produce some metrics.
Then, use the following curl command will fetch the metrics from your gateway:
curl -v http://localhost:4000/metricshttp://localhost:4000 to the actual URL of your running gateway.Customizations
By default, all operations are instrumented, including introspection queries. It is possible to
ignore introspection queries for all metrics prefixed by graphql_envelop_ by setting the
skipIntrospection option to true.
StatsD
You can use @graphql-mesh/plugin-statsd plugin to collect and send metrics to Datadog’s DogStatsD
and InfluxDB’s Telegraf StatsD services.
npm i @graphql-mesh/plugin-statsdCompatible with:
- Datadog’s DogStatsD server
- InfluxDB’s Telegraf StatsD server
- Etsy’s StatsD serve
Available metrics:
graphql.operations.count- the number of performed operations (including failures)graphql.operations.error.count- the number of failed operationsgraphql.operations.latency- a histogram of response times (in milliseconds)graphql.delegations.count- the number of delegated operations to the sourcesgraphql.delegations.error.count- the number of failed delegated operationsgraphql.delegations.latency- a histogram of delegated response times (in milliseconds)graphql.fetch.count- the number of outgoing HTTP requestsgraphql.fetch.error.count- the number of failed outgoing HTTP requestsgraphql.fetch.latency- a histogram of outgoing HTTP response times (in milliseconds)
graphql prefix and add custom tags to the metrics.Usage Example
import { defineConfig } from '@graphql-hive/gateway'
import useStatsD from '@graphql-mesh/plugin-statsd'
export const gatewayConfig = defineConfig({
plugins: pluginCtx => [
useStatsD({
...pluginCtx,
// Configure `hot-shots` if only you need. You don't need to pass this if you don't need to configure it.
client: {
port: 8020
},
// results in `my-graphql-gateway.operations.count` instead of `graphql.operations.count`
prefix: 'my-graphql-gateway',
// If you wish to disable introspection logging
skipIntrospection: true
})
]
})Sentry
This plugin collects errors and performance tracing for your execution flow, and reports it to Sentry.
This is how it looks like in Sentry for error tracking:
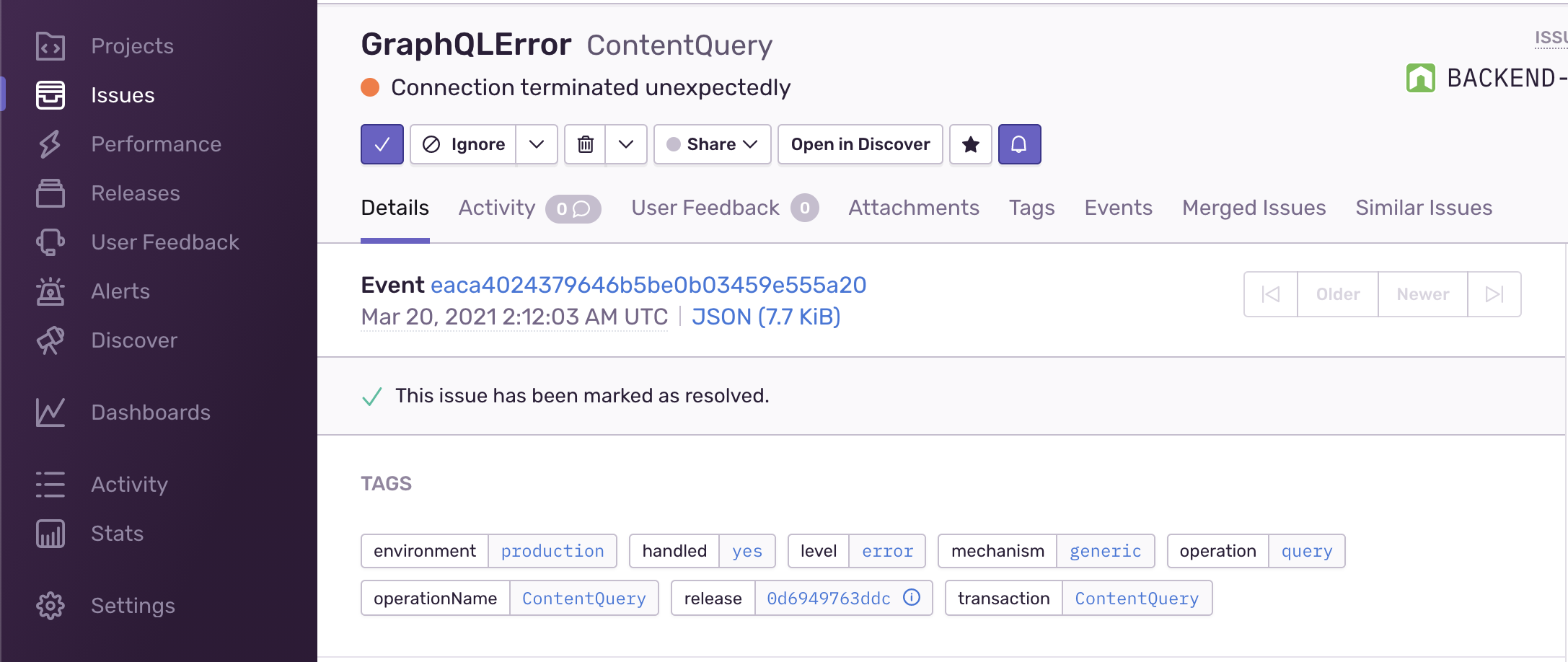
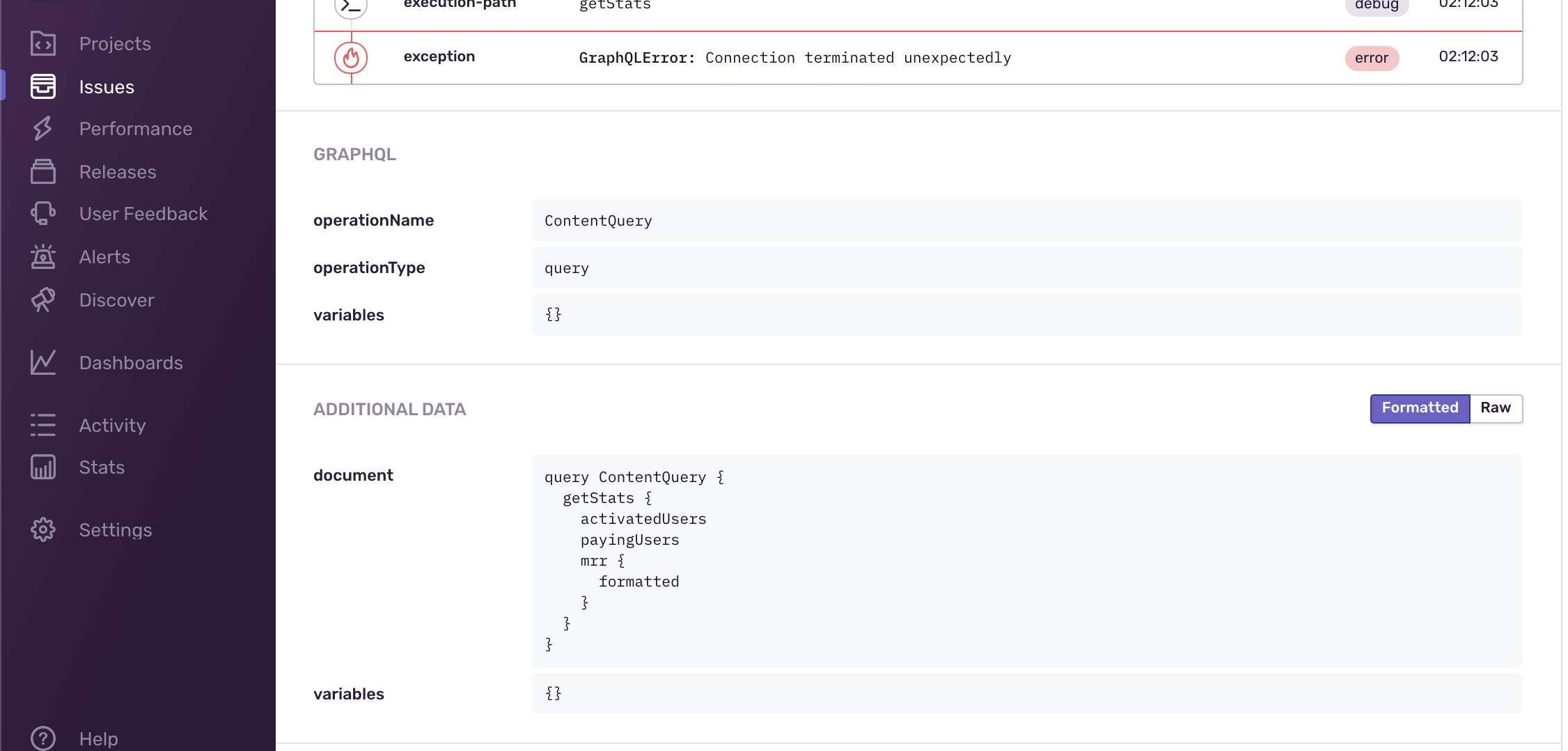
The operation name, document, variables are collected on errors, and the breadcrumbs that led to the error. You can also add any custom values that you need.
To get started with Sentry, you need to create a new project in Sentry and get the DSN:
- Start by creating an account and a project in https://sentry.io
- Follow the instructions to setup your Sentry instance in your application.
- Setup Sentry global instance configuration.
- Setup the Envelop plugin.
Then, install the following plugin in your project:
npm i @sentry/node @sentry/tracing @envelop/sentryUsage Example
import '@sentry/tracing' // import only once in you entry file!
import { useSentry } from '@envelop/sentry'
import { defineConfig } from '@graphql-hive/gateway'
export const gatewayConfig = defineConfig({
plugins: () => [
useSentry({
includeRawResult: false, // set to `true` in order to include the execution result in the metadata collected
includeResolverArgs: false, // set to `true` in order to include the args passed to resolvers
includeExecuteVariables: false, // set to `true` in order to include the operation variables values
appendTags: args => {}, // if you wish to add custom "tags" to the Sentry transaction created per operation
configureScope: (args, scope) => {}, // if you wish to modify the Sentry scope
skip: executionArgs => {} // if you wish to modify the skip specific operations
})
]
})Configuration
startTransaction(default:true) - Starts a new transaction for every GraphQL Operation. When disabled, an already existing Transaction will be used.renameTransaction(default:false) - Renames Transaction.includeRawResult(default:false) - Adds result of each resolver and operation to Span’s data (available under “result”)includeExecuteVariables(default:false) - Adds operation’s variables to a Scope (only in case of errors)appendTags- See example above. Allow you to manipulate the tags reports on the Sentry transaction.configureScope- See example above. Allow you to manipulate the tags reports on the Sentry transaction.transactionName(default: operation name) - Produces a name of Transaction (only when “renameTransaction” or “startTransaction” are enabled) and description of created Span.traceparentData(default:{}) - Adds tracing data to be sent to Sentry - this includes traceId, parentId and more.operationName- Produces a “op” (operation) of created Span.skip(default: none) - Produces a “op” (operation) of created Span.skipError(default: ignoredGraphQLError) - Indicates whether or not to skip Sentry exception reporting for a given error. By default, this plugin skips allGraphQLErrorerrors and does not report it to Sentry.eventIdKey(default:'sentryEventId') - The key in the error’s extensions field used to expose the generated Sentry event id. Set tonullto disable.